Ce site est en cours de reconstruction certains liens peuvent ne pas fonctionner ou certaines images peuvent ne pas s'afficher.
1.1. Introduction
1.1.1. What is R ?
According to the R-project site :
R is a language and environment for statistical computing and graphics. It is a GNU project which is similar to the S language and environment which was developed at Bell Laboratories (formerly AT&T, now Lucent Technologies) by John Chambers and colleagues. R can be considered as a different implementation of S. There are some important differences, but much code written for S runs unaltered under R.
R was created by Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman at the University of Auckland, New Zealand, and is currently developed by the R Development Core Team, of which Chambers is a member. R is named partly after the first names of the first two R authors and partly as a play on the name of S. The project was conceived in 1992, with an initial version released in 1995 and a stable beta version in 2000. (Ref Wikipedia)
Note that R is available as Free Software and runs on a wide variety of platforms: UNIX, Linux, Windows or MacOS.
R is made of 5 components:
- an effective data handling and storage facility (list, vectors, matrices, data.frame)
- a suite of operators for calculations on vector and matrices
- a large collection of intermediate tools for data analysis
- graphical facilities for data analysis
- a simple and effective programming language
All of this makes R very difficult to master all the more that the functions produce different results depending on the parameters provided.
1.1.2. How can I use R ?
You can either :
- use the text interface with the program R in a terminal
- use the Rscript program to execute scripts
- use the graphical interface called R-studio
- use the graphical interface Rcommander
1.1.2.a Terminal
For example if you execute R in a terminal you will get somehting like this and you will be in interactive mode: you have to type your calculation and press enter to get the result
richer@richer:~/dev/R/code$ R
R version 3.2.3 (2015-12-10) -- "Wooden Christmas-Tree"
Copyright (C) 2015 The R Foundation for Statistical Computing
Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu (64-bit)
R is free software and comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY.
You are welcome to redistribute it under certain conditions.
Type 'license()' or 'licence()' for distribution details.
Natural language support but running in an English locale
R is a collaborative project with many contributors.
Type 'contributors()' for more information and
'citation()' on how to cite R or R packages in publications.
Type 'demo()' for some demos, 'help()' for on-line help, or
'help.start()' for an HTML browser interface to help.
Type 'q()' to quit R.
[Previously saved workspace restored]
> q()
Save workspace image? [y/n/c]: y
You will have to type q() ↵ (where ↵ is the ENTER key on the keyboard) to quit R.
1.1.2.b RStudio
Here is what the interface of the free version of RStudio looks like under Ubuntu 16.04:
To install RStudio under Linux Ubuntu 16.04, follow this link.
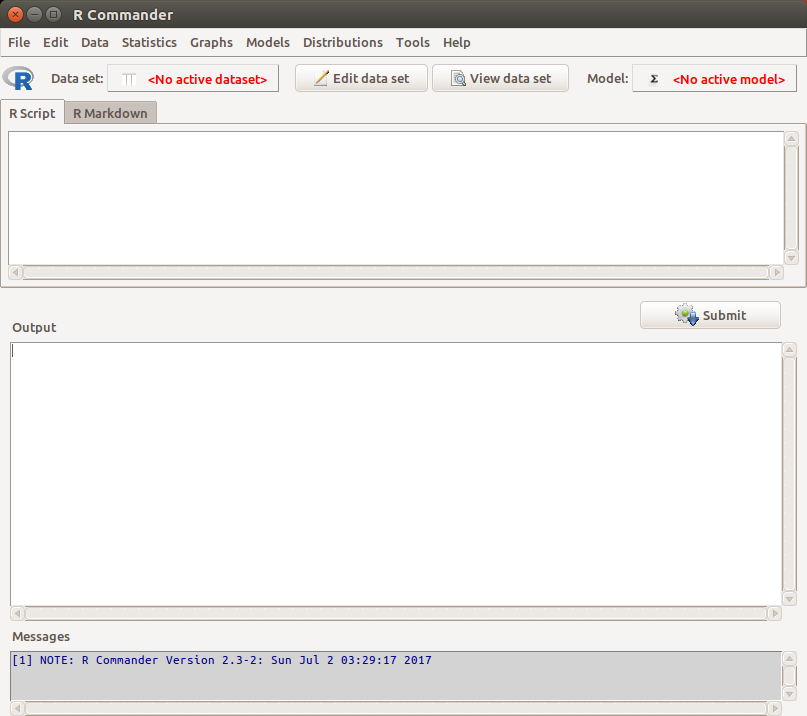
1.1.2.c RCommander - Rcmdr
Install and use Rcmdr as follows:
> install.packages("Rcmdr")
# run Rcmdr
> library("Rcmdr")
When you will run Rcmdr it will probably ask you to install some other packages.